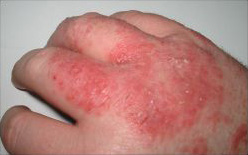
| English: Photograph of typical, mild dermatitis (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
The term Eczema is a medical term which is commonly used to describe a skin condition. In most cases, this skin condition is a type of dermatitis or an inflammation of the epidermis. The epidermis is the most outer layer of an individual's skin. Eczema is normally a persistent skin condition that causes dryness of the skin or rashes of the skin. Some of the most common symptoms of this skin condition are; skin redness, swelling or inflammation of the skin, itching skin, skin dryness, crusting or flaking of the skin, skin blisters, cracking of the skin, or bleeding or oozing of the skin. It is common for individuals with Eczema to experience slight skin discolorations. Normally, skin discolorations are the result of breakouts that are attempting to heal themselves. Scarring is rare in mild breakouts, but it can occur. Most scarring is a result from severe cases. Eczema is commonly mistaken for psoriasis. However, unlike psoriasis, it is most likely to be found on the flexor point of joints.
The different types of Eczema
The term "Eczema" is used to describe a broad set of characteristics. However, there are many different types of Eczema. In most cases, Eczema is classified by the location of the breakout. For instance, in an individual has an Eczema breakout on their hand area, the type of Eczema is referred to as "hand Eczema." Types of Eczema breakouts can also be classified by their physical appearance. For instance, if an individual has Eczema that displays multiple cracks in the area then the name of the Eczema would contain some sort of distinction that contains information about the cracks in the name.
There are numerous different types of Eczema breakouts.
The first type of Eczema is known as Atopic Eczema. Atopic Eczema is also called infantile, flexural, or atopic dermatitis. Atopic Eczema is an allergic disease believed to be caused by a hereditary trait. Atopic Eczema is common in individuals whose family suffers from hay fever and/or asthma. Most commonly, atopic Eczema is a rash that causes individuals a large amount of itching, especially on the head or scalp, neck, elbows, bend of the knees, and the buttocks region.
The second type of Eczema is known as contact dermatitis. Contact dermatitis has two main types: allergic and irritant. Allergic contact dermatitis normally results from a deferred reaction to an allergen. Irritant contact dermatitis results from a direct reaction from some sort of component such as a type of soap. Irritant contact dermatitis is responsible for about three quarters of all contact Eczema cases. Contact dermatitis is the most common skin disease today. The cure for contact Eczema is to simply avoid the object that the individual has contact with that sets off the Eczema. If the object that causes the Eczema is removed from the individuals contact, then the Eczema will normally disappear.
The third type of Eczema is known as Xerotic Eczema. Xerotic Eczema is also known as; asteatotic, craquele, or winters itch. Xerotic is a breakout where an individual has severe cases of dry skin. What happens in Xerotic Eczema is that the area of dry skin becomes so extreme and severe that the breakout turns in to Xerotic Eczema. This condition can become more severe during cold winter weather. In most cases of Xerotic Eczema, an individual's arms, legs, and core area are the regions most affected by this type of Eczema.
The fourth type of Eczema is known as Seborrhoeic dermatitis or Seborrheic dermatitis. In infants, this type of Eczema is called cradle cap. This type of Eczema is commonly related to dandruff. Seborrhoeic Eczema causes an individual to have greasy scalp, flaking or peeling of the scalp, flaking or peeling of the eyebrows, flaking and peeling of the face, and flaking and peeling of the trunk in some individuals. This type of Eczema is harmless for the most part, unless this type of Eczema occurs on an infant and develops into severe cradle cap.
Those are the most common types of Eczema. There are other types of this condition, but these types are less common. These less common types of Eczema are; Dyshidrosis which occurs on palms, fingers, and toes. Discoid Eczema, which is round rashes on the leg region that may have oozing. Venous Eczema is a type of Eczema that occurs in individuals with poor circulation, varicose veins, or edema. Venous Eczema is most common in the ankle area. Dermatitis herpetiformis is a type of Eczema that causes severe itches on an individual's limb, including the knee and thigh area, and the individuals back region. Neurodermatitis is a type of Eczema where a thick area of eczema is resultant of constant rubbing. Autoeczematization is a type of Eczema that results from an infection caused by a parasite, fungus, bacteria, or a virus.
Treatment for Eczema
As of today, there is still known cure for Eczema. However, there are numerous different types of treatments for Eczema which aim to maintain the breakout, reduce swelling or inflammation, and relieve itching or discomfort.
Eczema breakouts are frequently treated by using a corticosteroid medication. In most cases, the medication is in the form of an ointment, lotion, or cream. These types of medications do not cure Eczema breakouts but they are shown to cause an extreme improvement in the breakout. Corticosteroid medications work by reducing redness, relieving itching, and repressing other symptoms resultant of the Eczema.
There are various side effects to using corticosteroid medications to treat Eczema breakouts. If an individual uses the corticosteroid medications for an extended period of time, the chances of these side effects are likely to increase. Most commonly, an individual's skin will become thin or irritated if an individual uses the corticosteroid medication too long. Doctors normally prescribe a low dose of steroids to the individual to decrease this effect. These medications can cause cataracts when used on the face if the medication is used near the eye area. You may develop a fungal or bacterial infection if you do not use antibiotics or antifungal prescriptions in conjunction with your corticosteroid medication.
Immunomodulators were created to treat Eczema after corticosteroid treatments. Immunomodulators were developed to suppress the immune system where the Eczema breakout is located. The United States Food and Drug Administration have posted a health advisory about using Immunomodulators because there is a possibility of developing cancer of the lymph nodes or skin cancer.
Antibiotics are also used to treat Eczema. Some cases of Eczema become severe and develop cracks in the skin. Cracks in the skin allow bacteria to easily enter the body of the individual. Individuals who scratch their Eczema when it itches also cause infection, which can spread throughout the body. Antibiotics are used to treat these types of conditions related to Eczema.
Immunosuppressant is a treatment for Eczema. Doctors use immunosuppressants when an individual with Eczema does not respond well to other forms or methods of treatments. Immunosuppressants are used to weaken the immune system, which sometimes cause dramatic improvements in the condition of the individuals Eczema. Individuals who undergo immunosuppressants are required to have frequent blood screenings and be checked by their doctor on a regular basis.
Anti-itch medications or ointments are commonly recommended by physicians when an individual has Eczema. This is because most types of Eczema cause the individual to become itchy. Scratching the Eczema can cause infection, so to avoid itching doctors prescribe anti-itch medications.
Doctors also urge individuals to maintain a daily moisturizing routine to avoid dry skin. This is because Eczema can worsen when the individual's skin becomes dry. Keeping the skin moisturized is one of the most effective treatments an individual can perform themselves to provide relief and to help the area heal.
Doctors encourage individuals to avoid using harsh soaps, chemicals, and detergents. Individuals should replace these harsh items with moisturizing soaps, allergen controlled detergents, and chemicals that are less harsh on the skin. These harsh items can strip the natural oils off of the individual's skin and cause the skin to become severely dry or irritated. Individuals should take regular baths in an oatmeal formula. Individuals who suffer from Eczema should also avoid using powders and perfume because these products also cause the skin to become dry.
Preventing Breakouts
There are various things an individual can do in order to prevent a flare in their Eczema. Some of the most common Eczema prevention methods are to avoid using harsh soaps, harsh detergents, harsh chemicals, and powders. Begin purchasing moisturizing soaps to keep your skin moisturized. Individuals should also purchase detergents that have allergen control agents. Avoid using powders and perfumes altogether if at all possible. Powders and perfumes are notorious for stripping natural oils from the skin which cause the skin to become dry. If you use harsh chemicals to clean, make sure you begin wearing rubber gloves so that you can avoid exposing your skin to the agents in the cleaner. Avoid extreme temperatures, dry air, and irritating clothing.